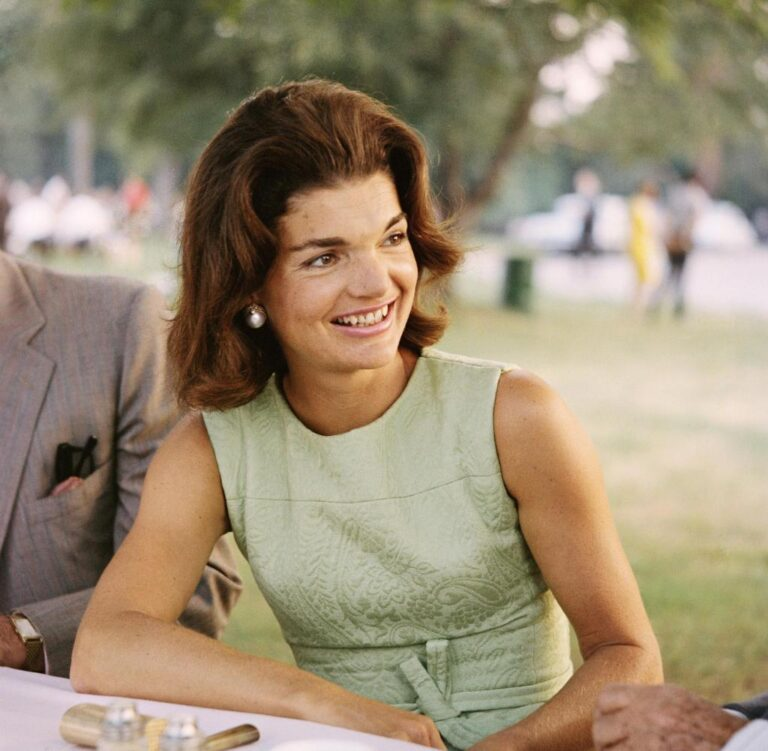

During her tenure in the White House, Jacqueline “Jackie” Kennedy rose to become one of the most adored First Ladies in history. For everyone seeing from the outside, the life of the Southampton, New York native and the then-youngest president to assume office—John F. Kennedy—seemed like a perfect love tale.
Everything changed on that dreadful November 1963 day in Dallas, Texas, when John F. Kennedy was shot and killed. Years later, Jacqueline, sometimes known as “Jackie,” would remarry after having to adjust to a completely new life.
Despite her enormous popularity, little was known about Jackie Kennedy’s existence in the White House; even though the people loved her, there were concerns regarding her availability on a daily basis.
New details about Jacqueline and her private life were disclosed by her former bodyguard, Clint Hill, in an interview with the JFK Presidential Library and Museum.

But first, let’s examine Jackie Kennedy’s life in more detail.
On July 28, 1929, in Southampton, New York, she was born Jacqueline Lee Bouvier. Her parents are Janet Lee and John Vernon Bouvier III.
Jackie Kennedy’s formative years
The Bouvier family was well-off, and her father was a stockbroker. At an early age, Jackie showed an interest in writing, painting, and riding. She was sitting on a horse’s back pretty much as soon as she could walk.
Due to her family’s financial stability, Jackie Kennedy attended some of the top private schools available. She spent her early years composing poetry and other stories and creating her own pictures for them while residing in New York City, Hampton, Newport, and Rhode Island. She studied ballet as well.
Jackie enrolled in Miss Chapin’s School on East End Avenue in New York’s first grade. Jackie was considered by Miss Platt, one of her instructors, to be “a darling child, the prettiest little girl, very clever, very artistic, and full of the devil,” according to the JFK Library.
By coincidence, Jackie got into a lot of trouble. “Jacqueline was given a D in Form because her disturbing conduct in her geography class made it necessary to exclude her from the room,” a headmistress Miss Ethel Stringfellow said on one of her report cards.
Jackie’s parents separated when she was ten years old, and her mother Janet later wed Hugh D. Auchincloss. Then, the family relocated to his house close to Washington, D.C.
Jackie Kennedy started attending Vassar College in 1947. She returned to George Washington University in 1951 to receive her degree after spending her junior year studying at the Sorbonne in Paris.

worked as a photographer and journalist.
Jackie developed empathy for individuals from other nations, particularly the French, as a result of her stay in France. She was unaware, nevertheless, that one day she would have the title of First Lady of the United States.
“It was the most beloved year of my life.” Of her year in France, Jackie Kennedy remarked, “Being away from home gave me a chance to look at myself with a jaundiced eye.”
“I came home happy to start over here but with a love for Europe that I’m afraid will never go,” the speaker said. “I learned not to be ashamed of a real hunger for knowledge, something I had always tried to hide.”
Jackie started her first employment at the Washington Times-Herald Newspaper after graduating from George Washington University. She adopted the persona of the “Inquiring Camera Girl,” going about the city during work hours, snapping pictures of individuals and posing various inquiries to them based on the topic of the day.
She kept on her column writing for the newspaper, conducting interviews with notable figures including Richard M. Nixon and covering Dwight D. Eisenhower’s first inauguration.

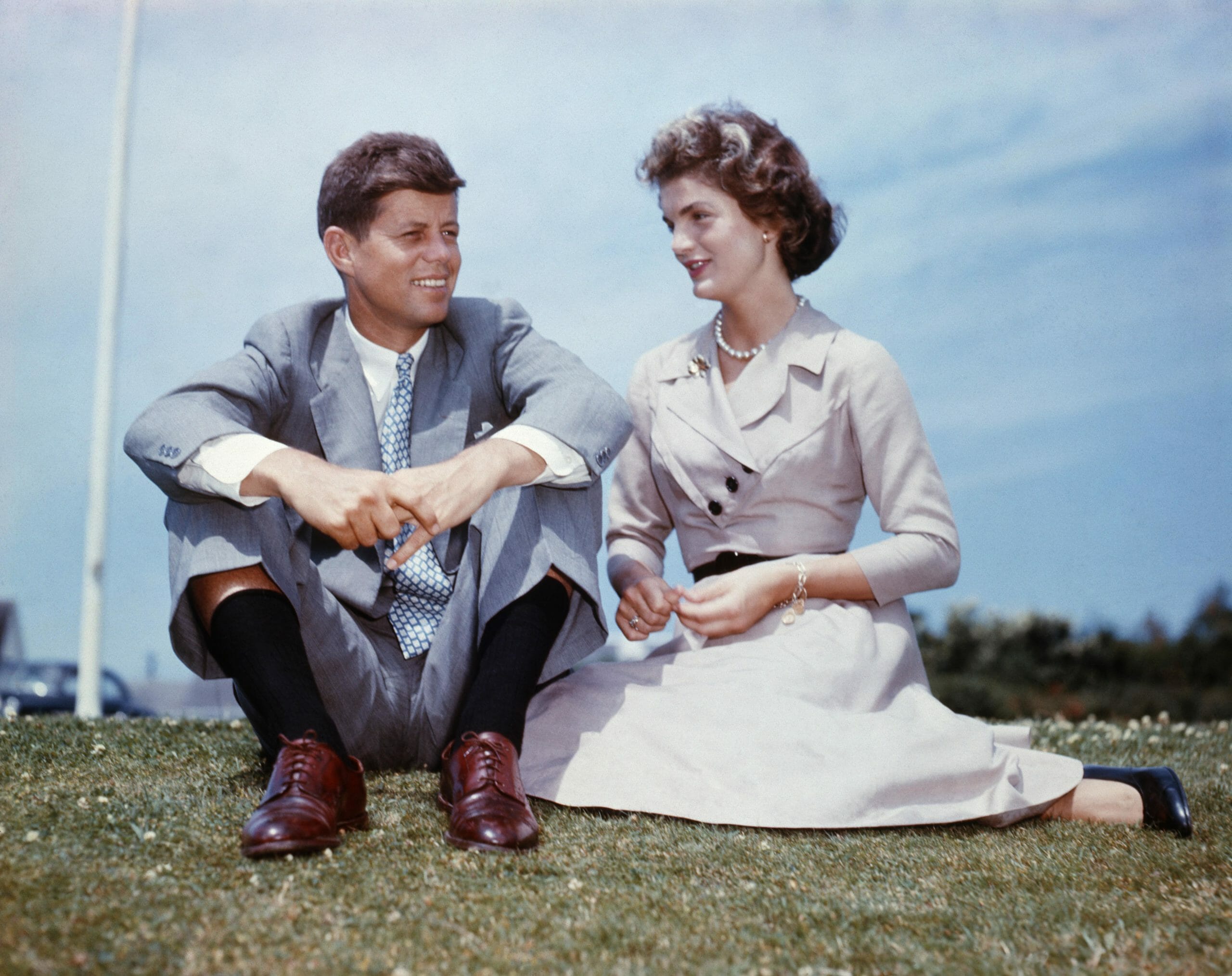
Jackie got to know John F. Kennedy, the man who would become her husband, at work at the Herald. She received an invitation to a dinner party in Georgetown in 1952, sent by Charles Bartlett, a friend and fellow journalist.
How did John F. Kennedy and Jackie Kennedy get together?
John Kennedy was a buddy of his as well. When they first met, Jackie and John clicked right away.
As stated in America’s Queen: The Life of Jacqueline Kennedy Onassis, Jackie’s family friend Molly Thayer remarked, “She knew instantly that he would have a profound, perhaps disturbing, influence on her life.”
At her rendezvous with future president John, sparks had already flown, even though Jackie left to go on another date. Ted Kennedy, his younger brother, said that he loved her.
When he first saw her at supper, “my brother really was smitten with her right from the very beginning,” he said.
Thus, it came to pass that Jackie and John F. Kennedy fell in love. The couple wed at St. Mary’s Church in Newport, Rhode Island, on September 12, 1953. Kennedy had already been elected to the U.S. Senate by the time they traveled to Mexico for their honeymoon.
JFK had plenty of free time at the same time that his political career was flourishing. During his recuperation from the back surgery, Jackie suggested that he publish a book about US senators who had sacrificed their careers to stand up for causes they supported.

Following the publication of Profiles in Courage, JFK was awarded the 1957 Pulitzer Prize for Biography. The birth of Caroline, the Kennedy family’s first child, made it a momentous year for them as well.
The life of Jackie Kennedy in the White House
A triennial later, Kennedy declared his intention to seek the presidency. JFK took over as the country’s next president on November 8, 1960.
Jackie, then thirty-one, was instantly crowned the First Lady of the United States. Her husband became quite upset shortly after the inauguration, and Jackie and JFK had a beautiful moment.
The pair was captured in the now-famous photo by AP photographer Henry Burroughs with Jackie’s palm resting on his chin.
“Why didn’t Jack kiss you after? Everyone asked, knowing full well that he would never do that there. Jackie Kennedy said, “But you had to march out in such an order that I was about eight behind him.”
And I really, really wanted to see him by himself before lunch. And I was just so proud of him when I finally caught up to him in the Capitol.
And there’s a photo where I put my hand on his chin and, you know, he’s just staring at me, and there were actual tears in his eyes,” she continued. I thought there was no one there, and then a flash occurred. The papers stated that his wife had chuckled him beneath the chin. That was so much more poignant than a kiss, in my opinion, because he actually did start to cry.

Jackie had a strong sense of duty to her nation. She was totally committed to their family at the same time, especially because John Fitzgerald Kennedy Jr., their second child, had been born a few weeks after the inauguration.
After the death of John F. Kennedy, life
The White House grounds were updated to include a swimming pool, a treehouse, and swings to better accommodate a family with young children. As First Lady, Jackie’s primary goal was to preserve and repair the White House.
After this was finished, Jackie Kennedy personally gave a tour of the facility. Over 80 million viewers tuned in to the CBS broadcast, and Jackie Kennedy received an honorary Emmy Award.
Patrick, John and Jackie’s third child, was born on August 7, 1963. Sadly, a serious lung condition claimed his life just two days later.
Then came the notoriously horrific Dallas, Texas, tragedy of November 22, 1963, when President Kennedy was shot and died. At the age of 34, Jackie became a widow, and millions of people worldwide expressed their sorrow.
Jackie was commended for her bravery and decency at the moment. She started working on the John F. Kennedy Presidential Library and Museum shortly after her husband passed away.

Jackie quickly stepped back from the spotlight and wed Greek shipping tycoon Aristotle Onassis in 1968. In 1975, she experienced her second divorce and made the decision to start a new profession. Jackie started off as an editor at New York City’s Viking Press before moving on to Doubleday as a senior editor.
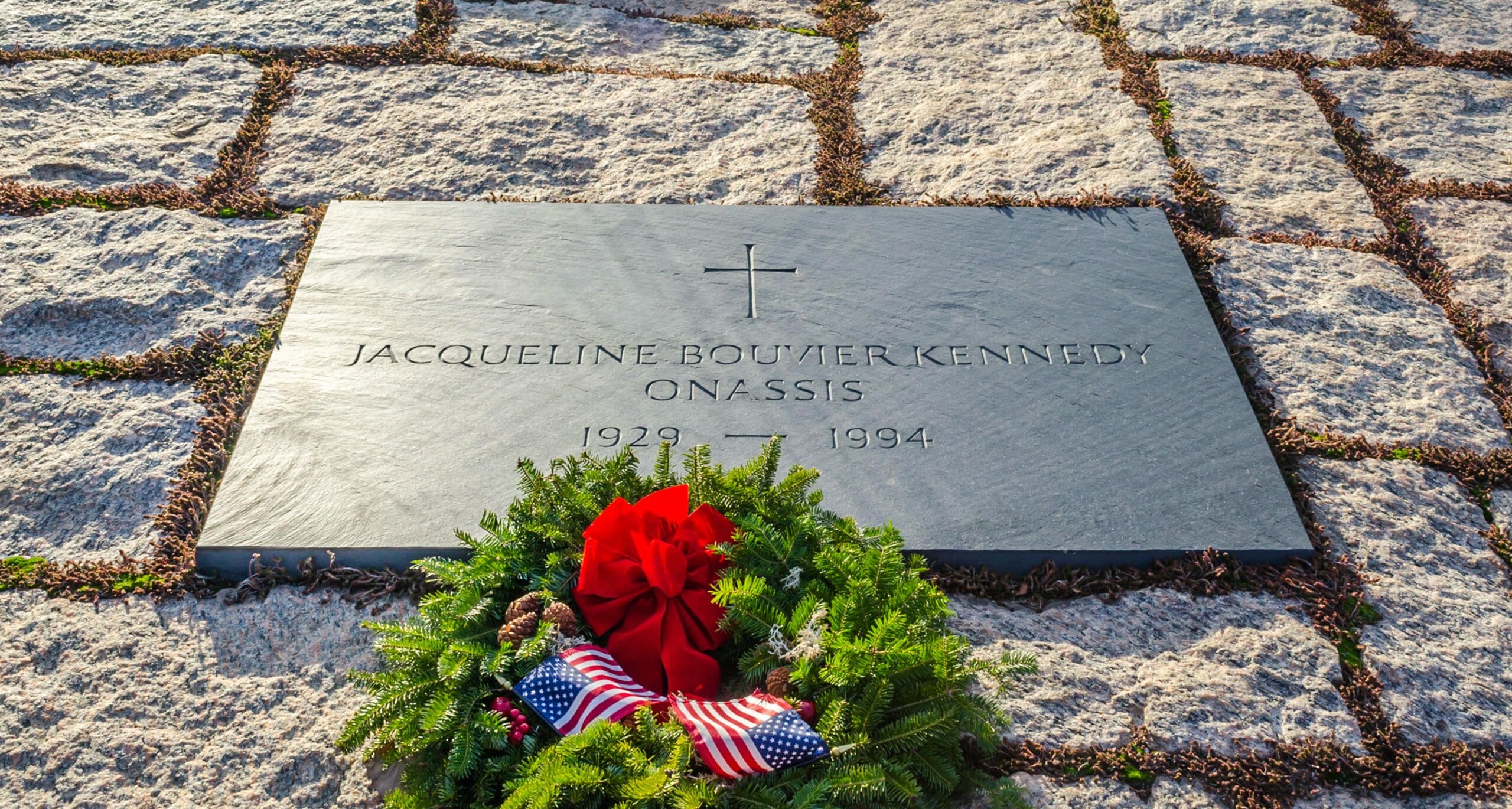
Cause of death: Jackie Kennedy
She died on May 19, 1994, of non-Hodgkins lymphoma, and was buried next to John F. Kennedy in Arlington National Cemetery, which is located outside of Washington, D.C.
All those who had known her as the First Lady were particularly hurt by her passing. However, not much is known about Jackie’s personal life, despite the fact that she rose to enormous popularity at the White House.
Clint Hill, her former bodyguard, recently opened up about his life defending Jackie, disclosing a lot of information that most people are probably unaware of.
Clint joined the Department of the Army as a counterintelligence agent and worked for President Eisenhower in Denver, Colorado. He was chosen one day to become an agent and collaborate closely with Jackie Kennedy.
He initially believed that would be a rather uninteresting detail.
“All right, we’ve made up our minds about what to do. You will be paired with Mrs. Kennedy. And I remember being extremely horrified,” Hill said.
“I was not interested in that task. I knew what prior first ladies were capable of. I had no desire to participate in fashion presentations, tea parties, or dance classes.
However, Clint quickly saw that Jackie was different from the other First Ladies who had come before her. The two struck up a wonderful friendship that progressively got better with time.

As previously stated, Jackie prioritized her children above everything else, serving as both a mother and a First Lady. Clint Hill also picked up on that very fast.
Clint Hill, a former bodyguard, describes Jackie Kennedy’s personality.
She desired that the kids grow up to be typical kids. Nothing noteworthy. They were to be handled by the agents as though they were one of their own. The children got back up if they fell. You failed to assist them. All of this has to be learned by them independently. He clarified, “She wanted to keep herself and the kids as anonymous as possible.
Yes, she made a fantastic mother. Her worries were centered around them and their schooling. In order to provide Caroline with an education, she established a school within the White House and invited several young students from various backgrounds to enroll as well. There were two teachers there, and it was located directly on the White House’s third level. He said, “They used to play out on the south grounds.”
Despite their intimate bond, Jackie always addressed Clint as Mr. Hill, while he addressed her as Mrs. Kennedy. He once moved his entire family to Squaw Island, where the Kennedy family was staying, for the duration of the summer.
As the First Lady’s bodyguard, Clint put in a lot of overtime and was frequently away from his family. As a result, his kids were essentially left fatherless.
However, Jackie occurred to observe that Clint’s kids were the same age as hers that summer on Squaw Island.

She asked Clint’s kids to come play with hers.
But as for him, he turned it down.
“She cared about us more than she did about herself.”
At last, I persuaded her by telling her that it wasn’t a good idea. In the government, I work. You are the president’s wife. These are the offspring of the President. Something should happen because I don’t think it would be a good idea for my two kids to play with your two kids. When she eventually realized what was wrong, she said, “Okay.”
Naturally, Clint Hill was there that awful November 1963 day in Dallas, Texas. He is recognizable in photos as the Secret Service operative who got into the automobile after JFK was shot.
Hill accompanied Jackie Kennedy to the hospital, and he was given credit for ensuring that no pictures were taken. He naturally desired to keep Kennedy’s privacy private. But she did something he didn’t anticipate when they got on the plane to return to Washington.
Instead of lamenting the death of her cherished spouse, Jackie Kennedy inquired about Clint Hill’s well-being.
“Oh, Mr. Hill, what’s going to happen to you now?” she exclaimed. Clint noted in the interview that “she was so much more concerned about my well-being and that of the other agents that were involved, that she wanted to make sure that we were going to be okay.”
“And I assured her, Mrs. Kennedy, I would be alright. I’ll be alright. She wasn’t dressed differently. She hadn’t tidy up. She was just shocked; she hadn’t done anything. Furthermore, she cared about us more than she did about herself.
A normal family showed their house and now everyone dreams of living there!
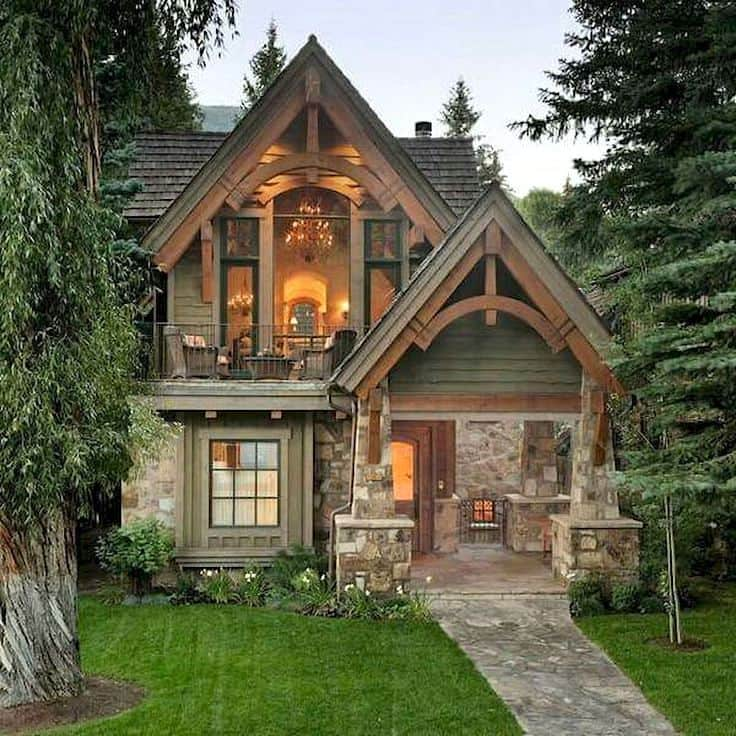
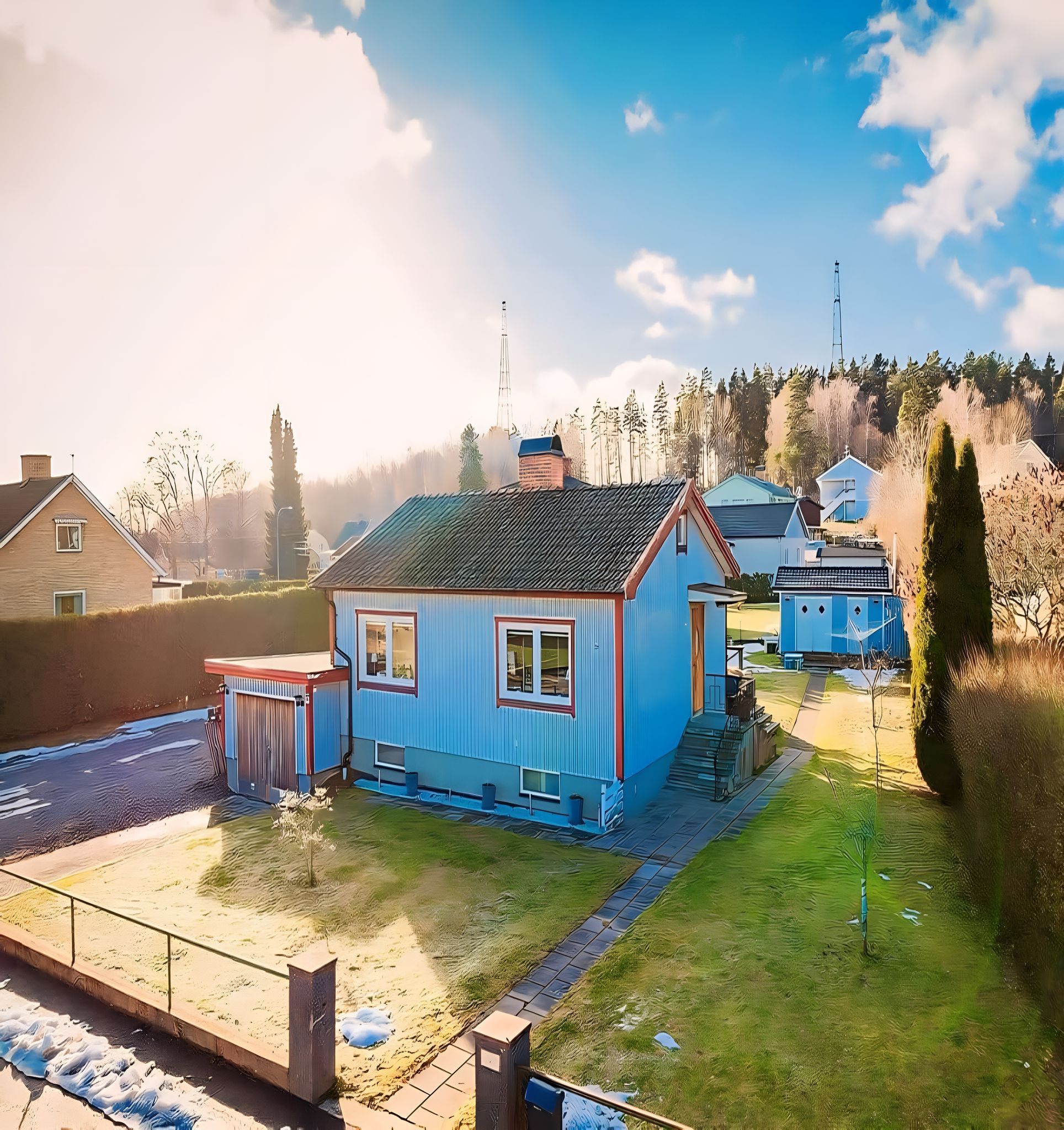


There are moments when it seems like we have seen everything that could possibly surprise us.However, there are things that none of us have missed and that we have not yet seen.Kindly focus on the house whose occupants are just regular folks.

The wife is a stay-at-home mom, and the husband is an engineer for a corporation.Due to the family’s low income, they raise two tiny children who do not even attend kindergarten.The young family has just been residing in the 1942-built house for the past four years.A seemingly typical house becomes a nature lover’s paradise and ideal haven.It comprises three fully functional rooms and is 56 square meters in size.

The living area, which is open to the kitchen, is where they congregate most often.It features two huge windows that give in plenty of natural light, a dining table, and contemporary furnishings.It’s not going to leave anyone unimpressed and has a fantastic view.Take a look and share your thoughts with us!


Leave a Reply