The tooth fairy is a welcome guest for any child who has lost a tooth. Not only will the fairy leave a small gift under the child’s pillow, but they be assured of a replacement tooth in a few months. Unfortunately, the scenario is quite different for adults grappling with a loss of teeth. Luckily, there may be some hope thanks to a new study performed by scientists at Kyoto University and the University of Fukui.
A dental breakthrough
While the typical adult mouth houses 32 teeth, approximately 1% of the population exhibits variations of them, either possessing more or fewer teeth due to congenital conditions. Researchers have delved into the genetic factors behind cases of excessive teeth, seeking valuable insights into the potential regeneration of teeth in adults. This study is the first to show that monoclonal antibodies can help regrow teeth. It suggests a new way to treat a dental problem that currently requires implants and other artificial solutions.
A bit of science
The research team disclosed that an antibody targeting a specific gene, known as uterine sensitization-associated gene-1 (USAG-1), can induce tooth development in mice affected by tooth agenesis, a congenital condition. The findings were published in the journal, Science Advances.
As per Katsu Takahashi, a senior lecturer at the Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine and one of the principal contributors to the study, the essential molecules crucial for the development of teeth have already been pinpointed. “The morphogenesis of individual teeth depends on the interactions of several molecules including BMP, or bone morphogenetic protein, and Wnt signaling,” says Takahashi.
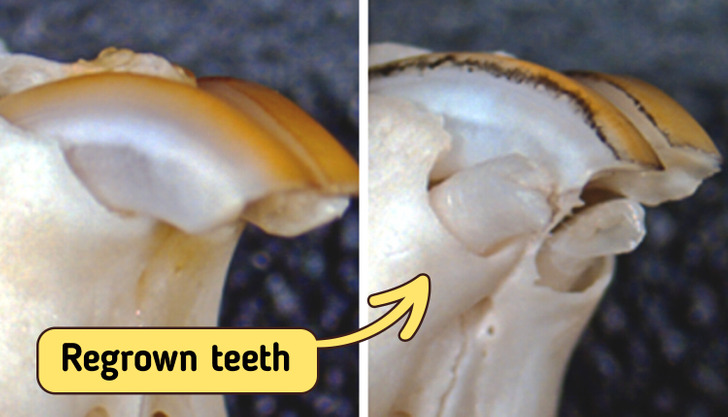
On April 13, 2021, the University of Kyoto posted its first pic of newly-grown teeth in mice.
BMP and Wnt are involved in more than just tooth development; they affect the growth of organs and tissues early in the body’s development. Because drugs affecting them directly might have broad side effects, scientists are cautious. To find a potentially safer method, researchers focused on the gene USAG-1, thinking that aiming at factors countering BMP and Wnt specifically in tooth development could be more precise.
“We knew that suppressing USAG-1 benefits tooth growth. What we did not know was whether it would be enough,” added Takahashi.
The first results
Scientists looked at how different monoclonal antibodies affect USAG-1. Monoclonal antibodies are often used to treat things like cancer and arthritis and for making vaccines. Tests with this antibody showed that BMP signaling is crucial for deciding the number of teeth in mice. Also, just one treatment was enough to grow a whole tooth. Further tests confirmed these positive results in ferrets too.
“Ferrets are diphyodont animals with similar dental patterns to humans. Our next plan is to test the antibodies on other animals, such as pigs and dogs,” explained Takahashi.
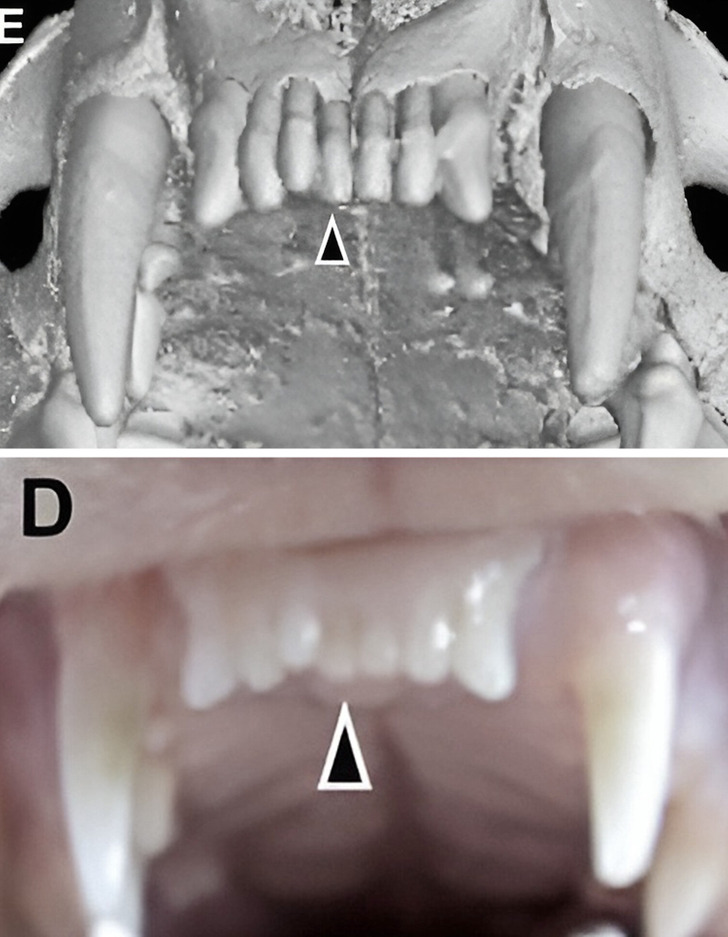
Fully regrown frontal teeth in ferrets
The next steps

Now, scientists are going to test the drug on healthy adults. If that goes well, the team plans to try it on kids aged 2 to 6 with a rare tooth problem called anodontia, a genetic disorder defined as the absence of all teeth. These kids will get one shot of the drug to see if it makes their teeth grow. If everything works out, the medicine might be approved by 2030.
Takahashi sees the new medicine as an additional choice for individuals who are missing some or all of their teeth.
“The idea of growing new teeth is every dentist’s dream,” Takahashi told the Japanese newspaper, The Mainichi in June this year. “I’ve been working on this since I was a graduate student. I was confident I’d be able to make it happen.”
So hopefully, by the year 2030, humans will get a chance to have their third generation of teeth grown and say goodbye to implants. Until then, make sure to keep your teeth strong and healthy — this article will help you with that.
Preview photo credit KyotoU_News / Twitter
Julia Roberts: Embracing her well-deserved vacation
No matter how much time passes by from the time the iconic movie that stole millions of hearts aired, stunning Julia Roberts would always be the Pretty Woman we all fall for.
At 56, the actress defies age, no matter what people think of her looks. For one, she’s all about natural aging and embraces her appearance.
The beloved Hollywood icon has been spotted enjoying a well-deserved vacation recently.
What many noticed is that Roberts gained a few pounds, but looking at her, we can’t help but agree that the saying “beauty comes in all shapes and sizes” is totally accurate.

The great thing about Roberts is that she’s not afraid to put on bikini despite those extra few pounds, and that’s one of the reasons we all love her so much.
Of course, people’s opinions over Robert’s recent photos differ. While some say she’s changed, others are convinced she looks stunning for her age, or any age to be honest.
Her fans always stay by her side and remind us that beauty doesn’t always come from the outside.

For the last 20 years, Roberts has been happily married to Daniel Moder. When they first met in 2000 on the set of The Mexican, Moder was married to then-wife Vera Steimberg. Rumors were that his first marriage broke down because of the Runaway Bride star although she claimed she wasn’t the reason why Moder and Steimberg divorced.

Before tying the knot with Moder, with whom she shared three children, twins Phinnaeus and Hazel and a son Henry, Roberts was romantically involved with actors Dylan McDermott, Matthew Perry, Jason Patric and Liam Neeson. She was briefly engaged to actor Kiefer Sutherland, but the two split mere days before they were supposed to say ‘I do.’
Roberts then married country singer Lyle Lovett and their marriage lasted for two years, from 1993 to 1995. At the time she met Moder, Roberts was said to have dated actor Benjamin Bratt.

Today, the couple are as in love as day one.



Leave a Reply